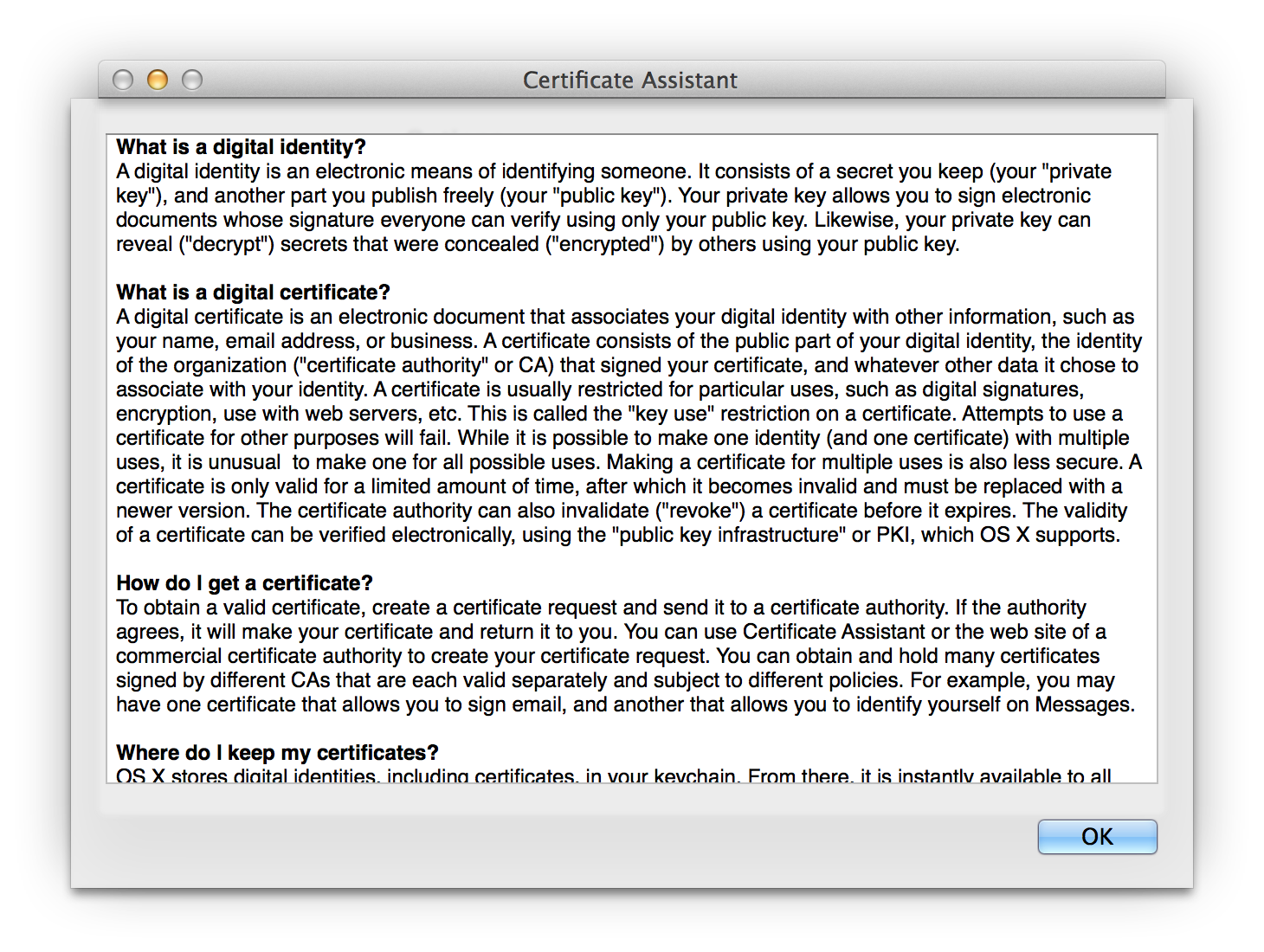
- What is a digital identity?
- 什么是数字身份?
- What is a digital certificate?
- 什么是数字证书?
- How do I get a certificate?
- 如何获得一个证书?
- Where do I keep my certificates?
- 证书保存在哪里?
- What is a Certificate Authority?
- 什么是证书颁发机构?
- Why evaluate certificates?
- 为何要评估证书?
一直对 iOS 的签名过程比较糊涂,搞不清楚每个步骤都做了些什么,特别是证书的请求过程。(这个过程现在清楚了,应该是生成了一个公钥、一个私钥,并将公钥发给苹果用于生成证书。)
使用的英文版的 OS X 翻看的 Centificate Assistant 时,发现其中对于证书的英文解释非常简单易懂,就开始翻译起来。翻译了两段之后才发觉自己比较愚钝,系统换成中文就能看到中文的解释。
中英对照列在下面,供大家参考学习。
What is a digital identity?
什么是数字身份?
A digital identity is an electronic means of identifying someone. It consists of a secret you keep (your “private key”), and another part you publish freely (your “public key”). Your private key allows you to sign electronic documents whose signature everyone can verify using only your public key. Likewise, your private key can reveal (“decrypt”) secrets that were concealed (“encrypted”) by others using your public key.
数字身份是一种用于识别某人的电子方式。它由您所持有的密钥(您的“专用密钥”)以及您可以自由发布的另一部分密钥(您的“公共密钥”)组成。您的专用密钥允许您签署每个人都仅能使用您的公共密钥来验证其签名的电子文稿。同样的,您的专用密钥能够显示(“解密”)被其他人使用您的公用密钥所隐藏(“加密”)的密钥。
What is a digital certificate?
什么是数字证书?
A digital certificate is an electronic document that associates your digital identity with other information, such as your name, email address, or business. A certificate consists of the public part of your digital identity, the identity of the organization (“certificate authority” or CA) that signed your certificate, and whatever other data it chose to associate with your identity. A certificate is usually restricted for particular uses, such as digital signatures, encryption, use with web servers, etc. This is called the “key use” restriction on a certificate. Attempts to use a certificate for other purposes will fail. While it is possible to make one identity (and one certificate) with multiple uses, it is unusual to make one for all possible uses. Making a certificate for multiple uses is also less secure. A certificate is only valid for a limited amount of time, after which it becomes invalid and must be replaced with a newer version. The certificate authority can also invalidate (“revoke”) a certificate before it expires. The validity of a certificate can be verified electronically, using the “public key infrastructure” or PKI, which OS X supports.
数字证书是一种能将您的数字身份同其它信息(如姓名、电子邮件地址或业务)联系起来的电子文稿。一份证书由数字身份的公共部分、签署证书的机构(“证书颁发机构”或 CA)的身份、以及它选取用来联系身份的任何其它数据所组成。证书通常被限制于特定的使用,例如数字签名、加密、用于 Web 服务器等。这被称为证书上的“密钥用途”限制。试图将证书用于其它目的的行为将会失败。尽管使一个身份(和一份证书)带有多个用途是可能的,但同一身份很少被制作成可用于所有可能的用途。将一份证书用于多个用途同样不太安全。一份证书仅在有限的时间段内有效,超过该时间段则会失效,而且肯定会被替换成更新的版本。证书颁发机构同样能使一张证书在其过期之前失效(“撤销”)。证书的有效性可以通过电子方式进行验证,方法是使用 OS X 支持的“公共密钥基础结构”或 PKI。
How do I get a certificate?
如何获得一个证书?
To obtain a valid certificate, create a certificate request and send it to a certificate authority. If the authority agrees, it will make your certificate and return it to you. You can use Certificate Assistant or the web site of a commercial certificate authority to create your certificate request. You can obtain and hold many certificates signed by different CAs that are each valid separately and subject to different policies. For example, you may have one certificate that allows you to sign email, and another that allows you to identify yourself on Messages.
若要获取一份有效的证书,请创建一份证书请求并将其发送到一家证书颁发机构。如果该颁发机构同意请求,它将会为您制作证书并将证书返回给您。您可以使用“证书助理”或商业证书颁发机构的网站来创建证书请求。您可以获取并保留由不同的 CA 签署的多张证书,每张证书都分别具有有效性且隶属于不同的政策。例如,您可能有一张证书来让您签收邮件,另一张则让您在 iChat 上进行自我识别。
Where do I keep my certificates?
证书保存在哪里?
OS X stores digital identities, including certificates, in your keychain. From there, it is instantly available to all your programs, including Mail and Safari. Likewise, certificates for others (mail correspondents, web sites, etc.) are also stored in your keychain as your computer obtains them for you. You can use Keychain Access (located in Applications > Utilities) to view and manipulate your certificates. You can move and copy certificates freely because they don’t contain personal or private information that you need to protect. It is all right to have several copies of one certificate. If you need to send a certificate to someone else, you can export it using Keychain Access and send it safely through email or by other means. Likewise, if someone sends you a certificate, you can add it to your keychain by dropping it onto Keychain Access, or using the Import menu in Keychain Access.
OS X 将包括证书在内的数字身份储存在钥匙串中。在这里,证书将能直接用于您的所有程序,包括“邮件”和“Safari”。同样的,其它对象(邮件收件人、网站等)的证书在电脑帮您获取之后,同样会储存在您的钥匙串中。您可以使用“钥匙串访问”(位于“应用程序”>“实用工具”)来查看和处理您的证书。您可以自由地移动和拷贝证书,因为证书并不包含您需要保护的个人信息或私密信息。为一份证书创建几个副本是完全可行的。如果您需要将证书发送给其他人,您可以使用“钥匙串访问”将其导出,并通过电子邮件或其它方式安全发送。同样的,如果某些人给您发送证书,您可以通过将它放置在“钥匙串访问”上或使用“钥匙串访问”中的“导入”菜单来进行添加。
What is a Certificate Authority?
什么是证书颁发机构?
A certificate authority (CA) is a digital identity that signs certificates and makes them valid electronic documents. Since CAs are digital identities themselves, they can also be validated by another CA, forming what is called a “certificate chain.” For a certificate to be valid, the CA that signed it must be valid, and so on up the chain. All this is automatically determined by OS X when it evaluates a certificate.
证书颁发机构 (CA) 是一个能够签署证书、并将它们制作成有效的电子文稿的数字身份。因为 CA 本身是数字身份,因此它们同样能被另一个 CA 验证有效性,这种形式被称为“证书链”。若一份证书有效,签署它的 CA 也必须是有效的,以此类推形成链状。所有这些都由 OS X 在评估证书时自动确定。
Why evaluate certificates?
为何要评估证书?
Use Certificate Assistant to evaluate the validity of a certificate and determine if it’s genuine. Secure software, such as Safari or OS X Mail, evaluates certificates before using them. For example, if you use Safari to purchase something online, Safari evaluates the web site’s certificate and lets you know if it’s valid. Certificate Assistant provides more detail and offers you more control over the use of certificates.
使用“证书助理”来评估证书的有效性并确定它是否真实。具有安全保障的软件,如 Safari 或 OS X 邮件,会在使用证书之前对它们进行评估。例如,如果您使用 Safari 在线购物,Safari 会评估该网站的证书并让您知道证书是否有效。证书助理会提供更多的详细信息,并为您提供证书用途之外的更多操作。
- EOF -